Volume 2, Issue 1
Evaluation of Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities from 28 Chinese Herbal Medicines
Author(s): Cheng-Hong Yang, Hsueh-Wei Chang, Ho-Yang Lin, Li-Yeh Chuang*
Institute of Biotechnology and Chemical Engineering, I-Shou University, 840 Taiwan
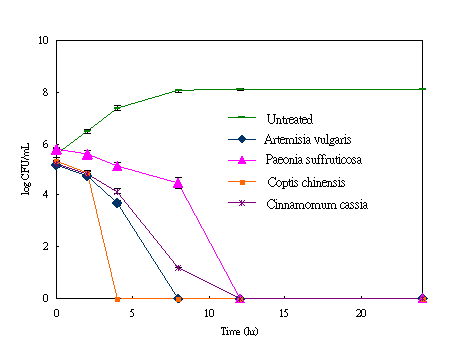
Abstract: Background: Many Chinese medicines have been reported to exhibit high antimicrobial and antioxidantactivities. In this study, 28 traditional Chinese herbal medicines were tested for their antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Materials and Methods: Total flavonoid content of the ethanol extracts were determined by a colorimetric method. Total phenol content was estimated as gallic acid equivalents. The antioxidant activities of the extracts were evaluated by various antioxidant assays, including 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging, trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) and reducing power. In addition to the antioxidant activity, the antimicrobial assay was measured as well. Six strains of the clinical antibiotic resistant pathogens including Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, methicine resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), ornithine resistant Staphylococcus aureus (ORSA), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii were used in the tests. Results: Among the extracts screened, Artemisia vulgaris and Sanguisorba officinalis showed the best antioxidant performance in all the tested methods.In vitro antibacterial activity, the extracts of Paeonia suffruticosa and Cinnamomum cassia displayed a broad antimicrobial spectrum and significantantimicrobial activities, with inhibition zones between 14-28 mm, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) between 0.9-5.2 mg/mL, and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) between 1.0-5.7 mg/mL. Conclusion: These data suggest that Artemisia vulgaris and Sanguisorba officinalis may be effective potential sources of natural antioxidants, and Paeonia suffruticosa and Cinnamomum cassia are potent inhibitors of antibiotic resistant pathogens.
Related Graphics:
Download Full Article : Click Here
